Quantum Theory
The quantum theory of the atom was developed to explain a phenomenon in the natural world, where sub-atomic particles called electrons normally remain in a wave–particle-wave function orbital path around/through the nucleus of an atom.
This phenomenon could not be explained by classical mechanics laws, such as Newton’s laws of motion and some of Maxwell’s laws of classical electromagnetism.
An electron orbiting an atom’s nucleus has quantized values of energy and angular momentum. An unbound electron does not show quantized energy levels, but is associated with a Compton wavelength, as are all particles.
This wave-function is a complex mathematical function of time and space (vector space) that can provide information about the position and momentum of a particle in an actual experiment, but only as a probability within the rules of the uncertainty principle.
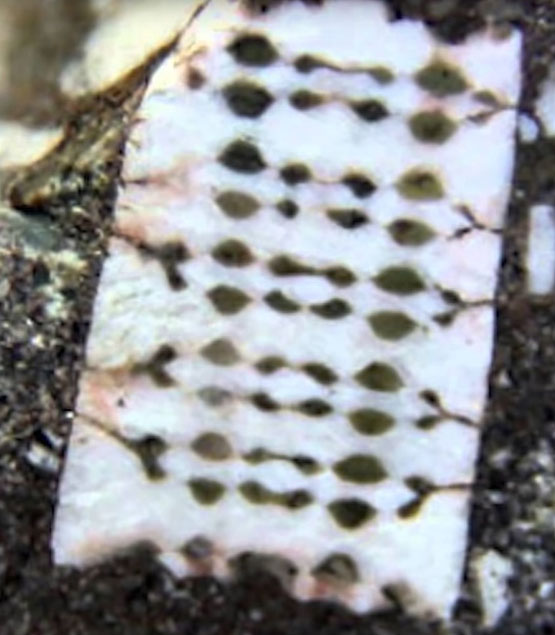

"Chip" embedded in 250 million years old rock
When parallel worlds interact, Quantum Mechanics and Quantum Conditioning are born
Many of the results of Quantum Mechanics can only be expressed mathematically. There are no models that are as easy to visualize as those of classical mechanics.
The chief problem is reconciling the many possibilities for a quantum particle's state, encoded in its wave function, with the fact that we can only observe one of them at the time.
The Born rule calculates the probability that a measurement of a quantum system or state will yield a given result: the square of the amplitude at the moment of observation, its entanglement:

US physicist Hugh Everett's interpretation made in 1957 is, that all those possibilities encoded in Schrödinger's wave function are actualities that play out in parallel realities.
We observe, perceive, become entangled, and interact, with only one of these possibilities because we are confined to one reality, meaning one branch of this wave function:
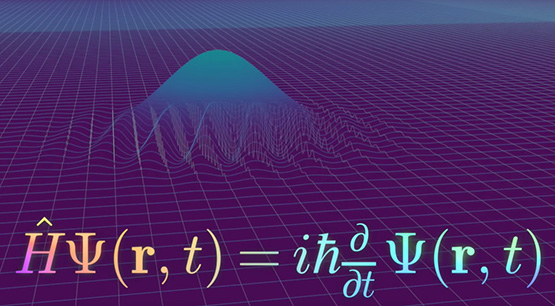
That wave function, with all its parallel strands as multiple-worlds, is the multiverse, the ultimate reality. One quantum object in a superposition is just one strand. The many worlds interpretation (MWI) states that every time a "random" event takes place, the universe splits between the various options available. Each separate version of the universe contains a different outcome of that event. Instead of one continuous timeline, the universe looks more like a series of branches splitting off of a tree limb.
Another interpretation in which the wave function is real is the "collapse interpretation". Here, the wave function contains all possibilities until we send attention energy to one event inherent to the wave function, while the other possibilities seem to have disappeared, but in reality they just fail to interact with the other branches.
This is caused by environmental de-coherence, through dispersing the quantum coherence everywhere. Thus, we do not always need an attentive conscious mind to “observe” in order to keep the wave function in a state of collapse.
Quantum superpositions are not really destroyed by the environment, but to the contrary they are turning the whole world steadily into one big quantum state. So, de-coherence is not a loss of superposition but a loss of our ability to detect it, because we perceive ourselves inside a global quantum de-coherence Bubble!
Quantum Conditioning offers a way out of that bubble and regain that ability.
Are we as humans living in a computer simulated world,
that is limited only by the laws of physics as we know them,
but our essence exists simultaneously in a world beyond this?
Without the large variety of applications of Quantum Physics, such as all electronic equipment everywhere, video games, TV-screens, Internet, mobile phones, computers, 4IR, quantum-particles-photons-healing, etc., our current digitalized world CANNOT function without it anymore!!

Bio-resonance quantum-particle-light therapy
causes the elimination of pathogenic micro-organisms,
and uses inverse oscillation patterns to help
the organism re-align and re-harmonize itself.